Get Support
+91 9123517774

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Mining and Natural Resources - Your Gateway to a New Frontier
Exploring New Horizons in Mining and Natural Resources the world of Mining and Natural Resources, an exciting new venture marked by fresh opportunities, innovation, and sustainability. In this introduction, we'll uncover the potential and significance of this industry and outline our commitment to making a positive impact as we embark on this journey.

Leaf Business Consulting Services
The Pivotal Role of Mining and Natural Resources
Mining and natural resources are the backbone of modern society, providing the essential raw materials that drive progress. From minerals that fuel industries to renewable energy sources, this industry underpins countless aspects of our daily lives. It is an industry that holds immense potential and significance.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
Understanding the Industry
Navigating the Landscape of Mining and Natural Resources
Business Aspects

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Resource Scarcity and Global Demand
The world's growing population and increasing urbanization are leading to a rising demand for essential resources such as minerals, metals, and energy sources. This demand is driven by sectors like infrastructure, manufacturing, and energy production, presenting opportunities for new entrants in the industry.
01.
Renewable Energy Transition
With the global focus on transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, there's a surge in demand for resources like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements for renewable energy technologies. Companies that can provide these resources sustainably stand to benefit from this transition.
02.
Technological Advancements
Mining and natural resource extraction are becoming more efficient and environmentally friendly due to technological advancements. Newcomers can leverage cutting-edge technologies to improve resource extraction and minimize environmental impact, making their operations more competitive.
03.
Environmental Responsibility
Environmental regulations and societal pressure are pushing the industry toward more responsible and sustainable practices. Companies that lead in environmentally friendly resource extraction and reclamation have a competitive edge and can cater to the growing market for eco-conscious consumers.
04.
Infrastructure Development
Emerging economies and developing nations are investing heavily in infrastructure development. This requires significant quantities of resources such as aggregates, cement, and steel. New players in the industry can tap into these markets to support global infrastructure projects.
05.
Mineral Exploration and Discovery
Ongoing mineral exploration efforts continue to uncover new resource deposits around the world. Entrepreneurs and companies with a knack for discovering untapped resources can find valuable opportunities in these discoveries.
06.
Recycling and Circular Economy
As the world shifts toward a more circular economy, the recycling and repurposing of resources become vital. Businesses involved in resource recovery and recycling processes can thrive in an era where resource efficiency is paramount.
07.
Global Economic Growth
The overall growth of the global economy has a direct impact on resource demand. As economies expand, they require more resources for construction, manufacturing, and energy production. Companies in the industry can capitalize on this economic growth.
08.
Collaboration and Innovation
Collaboration between mining companies, technology providers, and sustainability-focused organizations can lead to innovative solutions that enhance resource extraction and management. New entrants can leverage these collaborations to drive growth.
09.
Local and Global Partnerships
Developing partnerships with local and international entities can open doors to accessing resources, expertise, and markets. Newcomers can benefit from these connections to expand their presence in the industry.
10.
Proven Expertise
With a team of seasoned professionals, we bring extensive experience to every project, ensuring quality and efficiency.
11.
Innovation Leadership
We're at the forefront of technological advancements, consistently offering cutting-edge solutions for your business.
12.
Sustainability Focus
We are deeply committed to sustainable practices and environmental responsibility, promoting a brighter future for all.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
Benefits of a Client-Centric Approach in the Mining Industry

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Resource Scarcity and Global Demand
A client-centric approach in the mining, metal, and natural resource industry goes beyond extracting resources; it involves responsible and collaborative practices that prioritize the well-being of clients, communities, and the environment.
In the mining and metals industry, various software products are utilized to streamline operations, manage resources, and optimize processes.
Our Services
software products commonly used in mining and metals
MineSight
MineSight, now part of Hexagon Mining, is a comprehensive modeling and mine planning software suite used for geological modeling, mine design, and scheduling.
Surpac
Surpac, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is a popular software for geological modeling and mine planning. It includes modules for resource estimation, block modeling, and mine design.
Vulcan
Vulcan, developed by Maptek, is a 3D modeling and mine planning software widely used in the mining industry. It includes tools for geological modeling, mine design, and scheduling.
Datamine Studio
Datamine Studio is a mining software suite that includes modules for geological modeling, resource estimation, mine planning, and production scheduling.
Gemcom Surpac
Gemcom Surpac, now part of Dassault Systèmes, is a software suite for geological modeling, mine design, and planning in the mining and metals industry.
Deswik Suite
The Deswik Suite includes software for mine planning, design, and scheduling. It is known for its integrated approach to geological and mine planning.
MICROMINE
MICROMINE provides software solutions for geological exploration, resource estimation, mine planning, and production control in the mining and metals industry.
Maptek I-Site Studio
I-Site Studio, developed by Maptek, is used for laser scanning and modeling in the mining industry, allowing for precise surveying and analysis.
Mintec MineSight 3D
Mintec MineSight 3D is a modeling and visualization software used in geological and geotechnical applications in the mining sector.
WISP
WISP is a strategic mine planning software that aids in optimizing pit design, scheduling, and financial modeling.
Bentley OpenMine
Bentley's OpenMine software provides tools for mine planning and design, helping mining professionals optimize production and reduce costs.
Aegis Mining Software
Aegis is a software solution designed for the mining industry, offering modules for geological modeling, resource estimation, and mine planning.
Geovia Surpac Quarry Edition
Geovia Surpac Quarry Edition is tailored for quarry and aggregate operations, providing tools for geological modeling, resource estimation, and mine planning.
Gemcom Minex
Gemcom Minex is a geology and mine planning software designed for the coal mining industry, offering tools for geological modeling and mine design.
GOCAD Mining Suite
GOCAD Mining Suite is used for 3D geological modeling and visualization in the mining industry.

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Software development in the natural resources sector involves creating tools and applications to assist with the exploration, extraction, management, and sustainable use of natural resources. Here are some areas within natural resources and related software products
01.
GIS Software
ArcGIS: ArcGIS is a powerful Geographic Information System (GIS) software used for mapping, spatial analysis, and managing geospatial data. It's widely employed in natural resources management, environmental monitoring, and land use planning.
QGIS (Quantum GIS): QGIS is an open-source GIS software that provides similar functionalities to ArcGIS. It's used for mapping, spatial analysis, and data visualization.
02.
Mining Software
Surfer: Surfer, developed by Golden Software, is used for 3D surface mapping and visualization. It's employed in geological mapping and resource estimation in the mining industry.
Datamine Studio: Datamine Studio is a suite of mining software used for geological modeling, resource estimation, and mine planning.
Maptek Vulcan: Vulcan is a 3D modeling and mine planning software suite specifically designed for the mining industry.
03.
Forestry Software
Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) Tools: Various tools and software are used for forest inventory and analysis, helping in the sustainable management of forest resources. These tools often include GIS functionalities for spatial analysis.
04.
Water Resource Management
HEC-RAS (Hydrologic Engineering Center's River Analysis System): Developed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, HEC-RAS is used for river and stream channel hydraulics and floodplain analysis.
MODFLOW: MODFLOW is a widely used groundwater modeling software for simulating and managing groundwater flow.
05.
Oil and Gas Software
Petrel: Petrel, developed by Schlumberger, is a software platform used in the exploration and production of oil and gas. It integrates geological, geophysical, and reservoir engineering data.
Kingdom Suite: The Kingdom Suite, developed by IHS Markit, is used for seismic interpretation and reservoir modeling in the oil and gas industry.
06.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Software
ESRI's ArcGIS for Environmental Management: GIS software is often used in EIA for mapping environmental features, analyzing spatial relationships, and assessing potential impacts.
Impact Assessment and Planning (IAP) Software: Various software solutions are used for comprehensive impact assessment and planning, helping ensure sustainable resource development.
07.
Precision Agriculture Software
Farm Management Software: Various software products assist farmers in optimizing crop yields, managing resources efficiently, and making data-driven decisions.
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing Tools: These tools help monitor crop health, assess soil conditions, and provide valuable information for precision agriculture
08.
Renewable Energy Software
Wind Farm Design Software: Tools for designing and optimizing the layout of wind farms, considering factors like wind speed, terrain, and environmental impact.
Solar Energy Modeling Software: Software used for simulating and optimizing solar energy production, considering factors like sunlight intensity, shading, and panel orientation.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable source of power that harnesses sunlight to generate electricity or heat. It is a clean and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels

01.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Technology
Solar Cells: Photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar cells, convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Solar Panels: Solar panels consist of interconnected solar cells and are used to capture and convert sunlight into electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
02.
Solar Thermal Technology
Surfer: Surfer, developed by Golden Software, is used for 3D surface mapping and visualization. It's employed in geological mapping and resource estimation in the mining industry.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, generating heat that can be used to produce steam and drive turbines for electricity generation.
Solar Water Heating: Solar thermal collectors can also be used to heat water for residential or industrial purposes.
03.
Applications of Solar Energy
Residential Solar Power: Rooftop solar panels for homes, providing clean energy and reducing reliance on the grid
Solar Street Lighting: Solar-powered streetlights for energy-efficient outdoor lighting.
Solar Water Pumping: Using solar energy to power water pumps for irrigation or community water supply.
Solar-Powered Vehicles: Development of electric vehicles powered by solar energy.
04.
Advantages of Solar Energy
Renewable and Sustainable: Solar energy is an abundant and renewable resource, making it sustainable for long-term use.
Low Environmental Impact: Solar power generation has a low environmental impact, producing no greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
Reduced Energy Bills: Solar panels can significantly reduce electricity bills for homes and businesses.
Job Creation: The solar industry provides job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
4 Challenges and Considerations
01.
Technological Advancements
Solar Efficiency Improvements: Ongoing research focuses on improving the efficiency of solar cells to capture more sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Flexible Solar Panels: Development of flexible and lightweight solar panels for versatile applications.
Solar Tracking Systems: Tracking systems that follow the sun's path for increased energy capture throughout the day.
02.
Global Impact
Climate Change Mitigation: Solar energy plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
03.
Educational and Community Initiatives
Public Awareness Programs: Educational initiatives to increase public awareness about the benefits of solar energy and its role in sustainability.
Community Solar Projects: Collaborative solar initiatives that allow communities to share the benefits of solar power.
04.
Future Outlook
Emerging Technologies: Exploration of emerging technologies, such as perovskite solar cells and solar paint, for enhanced efficiency and new applications.
Integration with Other Renewable Sources: Integration of solar energy with other renewable sources for a more reliable and consistent energy supply.

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Solar energy is a versatile and increasingly cost-effective solution for addressing energy needs while reducing the environmental impact. Continued advancements in technology, supportive policies, and increased public awareness will contribute to the widespread adoption of solar energy, playing a key role in the transition to a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
Energy-efficient buildings
Energy-efficient buildings are designed and constructed with the goal of minimizing energy consumption while providing a comfortable and productive environment for occupants. These buildings incorporate various technologies, design principles, and materials to optimize energy use.

01.
Key Features of Energy-Efficient Buildings
High Thermal Performance:Insulated building envelopes with materials that reduce heat transfer, promoting temperature stability.
Energy-Efficient Windows: Double or triple-glazed windows with low-emissivity coatings to minimize heat loss or gain.
Advanced Lighting Systems: LED lighting, daylighting strategies, and occupancy sensors to reduce electricity consumption.
Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems: High-efficiency heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems designed for optimal performance.
Renewable Energy Integration: Integration of on-site renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines.
Smart Building Technologies: Building automation systems to monitor and control energy use, optimizing operations based on occupancy and environmental conditions.
02.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Buildings
Reduced Energy Costs: Lower operational expenses due to decreased energy consumption.
Environmental Impact: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and environmental footprint.
Increased Comfort: Improved indoor environmental quality with consistent temperatures and better air quality.
Resilience to Energy Price Fluctuations: Reduced vulnerability to energy price volatility.
Enhanced Property Value: Energy-efficient features can increase the market value and attractiveness of a property.
03.
Design Strategies for Energy Efficiency
Passive Solar Design: Utilizing natural sunlight for heating and daylighting while minimizing solar heat gain.
Proper Insulation: Installing high-quality insulation materials to reduce heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors.
Efficient Lighting Design: Implementing energy-efficient lighting fixtures and controls to optimize natural and artificial lighting.
High-Efficiency HVAC Systems: Installing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) ratings.
Ventilation Strategies: Employing natural ventilation, heat recovery ventilation systems, or demand-controlled ventilation to enhance indoor air quality.
04.
Considerations for Energy-Efficient Buildings
Life-Cycle Cost Analysis: Evaluating the total cost of ownership, considering construction, operation, and maintenance costs over the building's lifespan.
Occupant Behavior: Educating and engaging building occupants in energy-saving practices.
Commissioning and Retro-Commissioning: Ensuring that building systems are installed and operate as intended during both initial construction and subsequent modifications.
Adaptability and Flexibility: Designing buildings with flexibility to accommodate changes in occupancy, technology, and space use.
Local Climate Considerations: Tailoring energy-efficient strategies to the specific climatic conditions of the building location.
05.
Certifications and Standards
LEED Certification: Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification provides a recognized standard for measuring building sustainability.
Energy Star Certification: Buildings meeting Energy Star criteria demonstrate superior energy performance.
Passive House Standard: A rigorous, voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, with a focus on reducing the building's ecological footprint.
06.
Government Incentives and Policies
Tax Credits: Financial incentives for implementing energy-efficient features.
Building Codes and Standards: Government regulations mandating specific energy efficiency requirements in building construction.
Energy Performance Contracts: Agreements between building owners and energy service companies to improve energy efficiency and performance.
07.
Technological Advances
Smart Sensors and Controls: Integration of advanced sensors and controls for real-time monitoring and optimization of energy use.
Energy Storage Solutions: Utilization of energy storage systems to store excess energy for use during peak demand periods.
Building Information Modeling (BIM): Use of BIM for comprehensive design, construction, and management of energy-efficient buildings.
Leaf Business Consulting Services
Energy-efficient buildings play a crucial role in addressing environmental concerns, reducing energy consumption, and creating comfortable and sustainable spaces. As technology advances and awareness of environmental issues grows, the design and construction of energy-efficient buildings will continue to evolve, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient built environment.
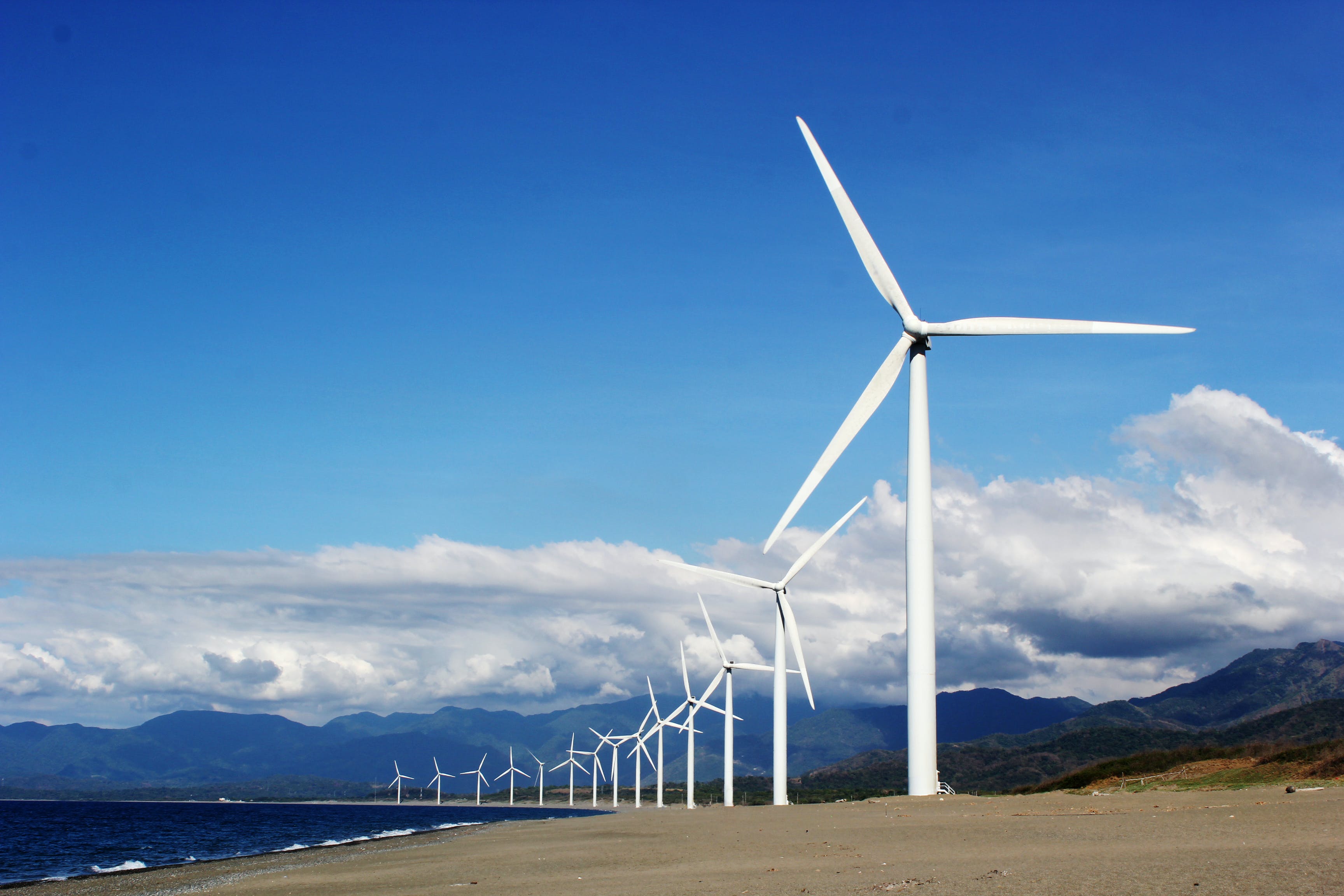
Wind power is a renewable and sustainable energy source that harnesses the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. It has become a significant contributor to global energy production, offering environmental benefits and reducing dependence on fossil fuels
Wind Turbine Technology

Onshore and Offshore Wind Farms

Applications of Wind Power
Advantages of Wind Power

Challenges and Considerations

Technological Advancements

Community Engagement

Government Policies and Incentives

Global Impact

Future Prospects

Leaf Business Consulting Services
Wind power continues to play a crucial role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. Advances in technology, supportive policies, and increased public acceptance contribute to the growing adoption of wind power globally, making it a key component of efforts to address climate change and achieve a more sustainable energy landscape.
Waste recycling is a critical component of sustainable waste management, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of waste by diverting materials from landfills and incinerators. It involves the collection, processing, and transformation of waste materials into new products.
Types of Waste for Recycling

Waste Collection and Sorting

Recycling Processes

Benefits of Waste Recycling

Challenges and Considerations

Innovations in Waste Recycling

Government Policies and Regulations

Community Engagement and Education

Waste-to-Energy Technologies

International Collaboration


Leaf Business Consulting Services
Waste recycling is a vital strategy for managing waste sustainably, conserving resources, and reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal. Ongoing innovations, public awareness campaigns, and supportive policies contribute to the growth of recycling efforts, fostering a more circular and sustainable approach to waste management.
Wanted Free Consulting ?
We are always ready to help you.


