In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, optimizing production processes is crucial for staying ahead. One approach that has proven to be highly effective is Lean Manufacturing. Rooted in the principles of continuous improvement and waste reduction, Lean Manufacturing is a philosophy that aims to maximize value while minimizing waste.
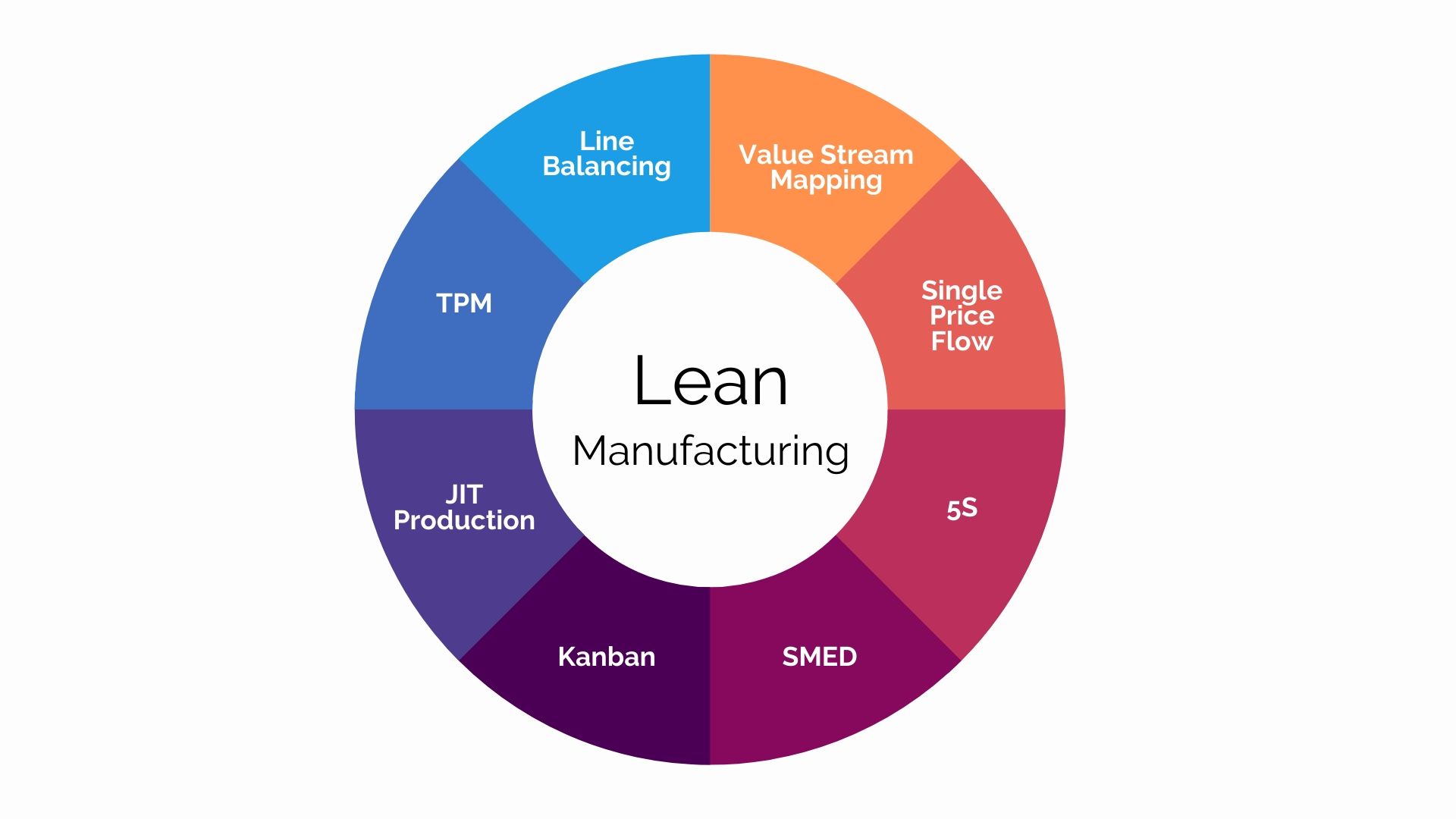
The Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing:
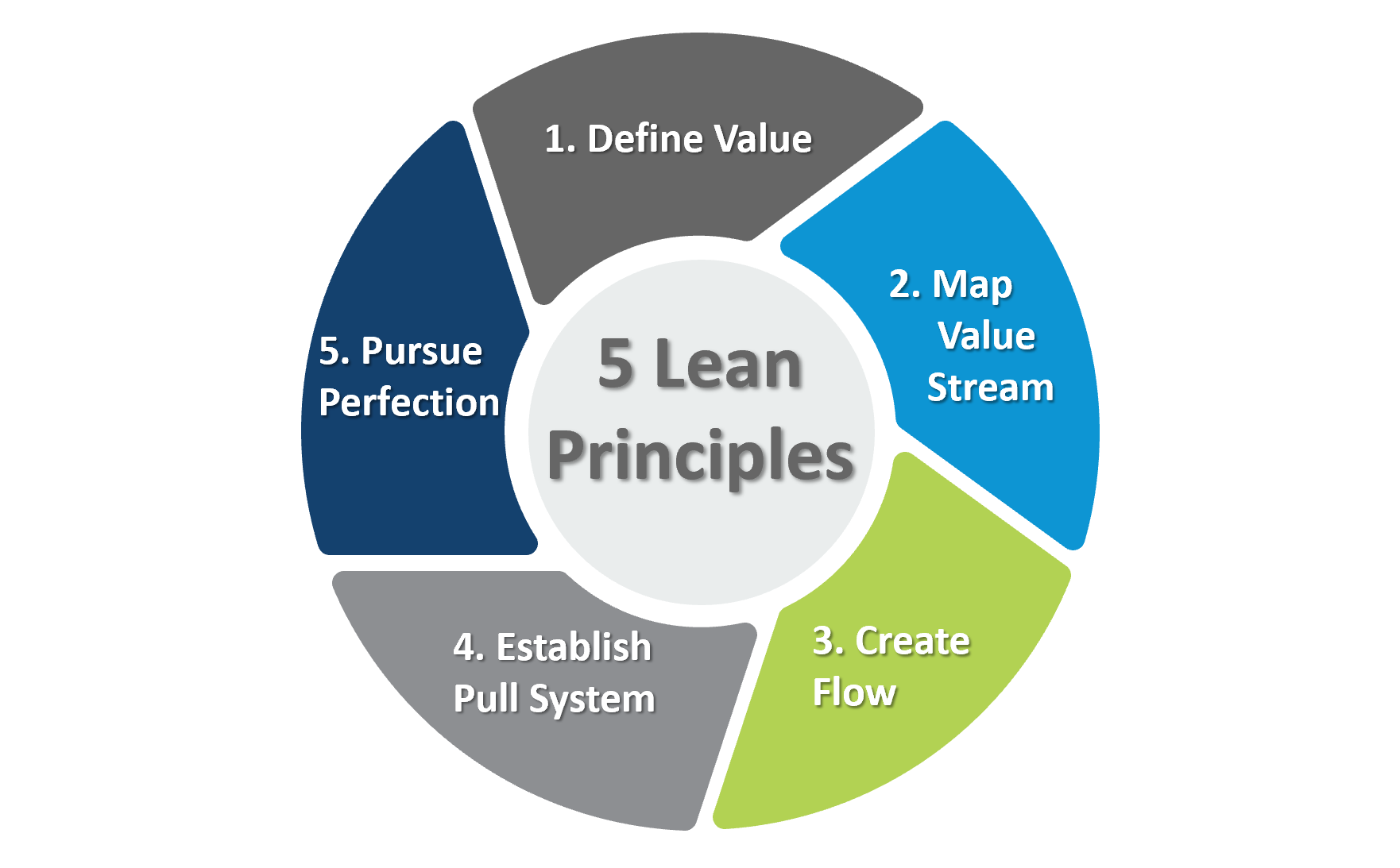
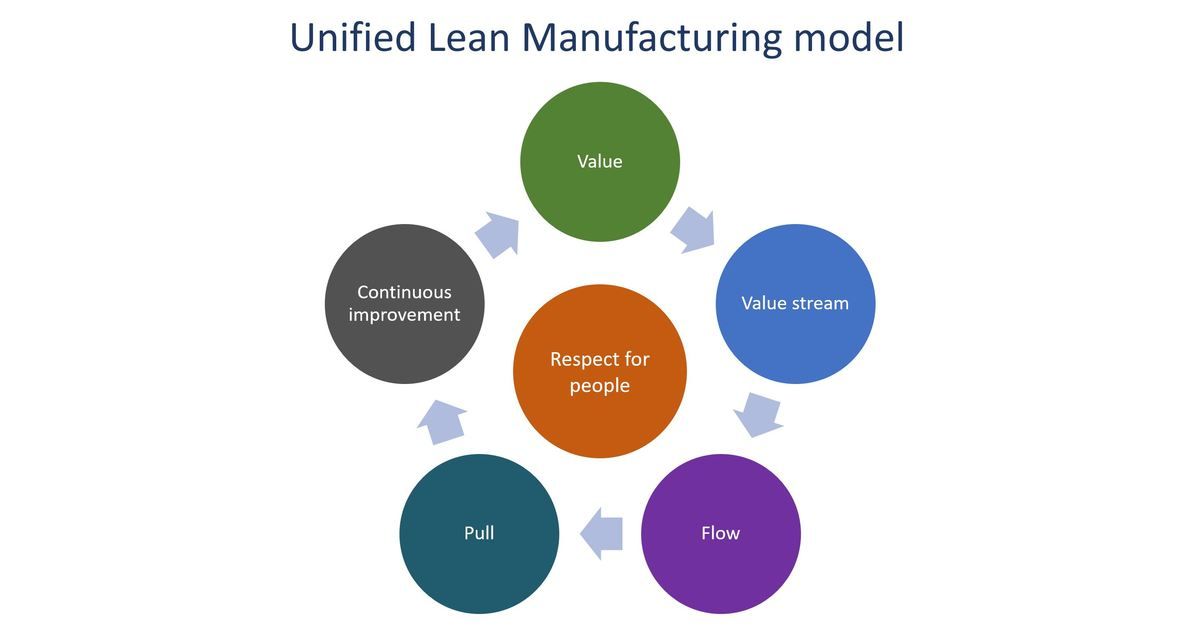
1. Value Identification: The foundation of lean manufacturing is understanding what adds value from the customer's perspective. This involves identifying the features and aspects of a product or service that customers are willing to pay for.
2. Value Stream Mapping: Once value is identified, the next step is mapping the entire value stream. This involves creating a visual representation of every step in the production process, from raw materials to the delivery of the final product.
3. Flow Optimization: Lean manufacturing emphasizes the importance of a smooth and continuous flow of work. By eliminating bottlenecks and optimizing the flow of materials and information, production processes become more efficient.
4. Pull Systems: Implementing pull systems ensures that production is demand-driven. Rather than pushing products through the process, a pull system responds to customer demand, reducing the risk of overproduction and excess inventory.
5. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Lean manufacturing is a journey of continuous improvement. The Kaizen philosophy encourages small, incremental changes over time, fostering a culture of constant enhancement in processes and systems.
6. Respect for People: People are a crucial element in lean manufacturing. By empowering employees, providing proper training, and fostering a culture of collaboration, organizations can tap into the collective knowledge and skills of their workforce.
Reducing Waste through Lean Principles:
One of the primary goals of lean manufacturing is the reduction of waste. Waste, in the context of lean principles, refers to anything that does not add value to the final product. There are seven types of waste identified in lean manufacturing:
1. Overproduction: Producing more than what is demanded leads to excess inventory and storage costs. Lean manufacturing aims to align production with actual demand.
2. Inventory: Excess inventory ties up capital and warehouse space. Lean principles advocate for just-in-time production to minimize inventory levels.
3. Defects: Defective products result in rework, scrap, and customer dissatisfaction. Lean manufacturing focuses on building quality into the process to reduce defects.
4. Waiting: Idle time during production or delays in processes contribute to waste. Lean principles aim to eliminate waiting times and ensure a continuous flow of work.
5. Transportation: Unnecessary movement of materials adds to costs and time. Lean manufacturing seeks to minimize transportation waste by optimizing the layout of production facilities.
6. Motion: Excessive movement of workers or machinery is considered wasteful. Lean principles focus on ergonomics and efficient layouts to minimize unnecessary motion.
7. Overprocessing: Performing more work than necessary or using overly complex processes contributes to waste. Lean manufacturing advocates for streamlined, efficient processes.
Realizing the Benefits of Lean Manufacturing:
Implementing lean manufacturing principles brings about numerous benefits for organizations:
- Increased Efficiency: Lean practices lead to streamlined processes, reducing lead times and improving overall efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing waste and optimizing resources, organizations can significantly reduce operational costs.
- Enhanced Quality: The focus on building quality into processes helps in the production of defect-free products, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Improved Flexibility: Lean manufacturing makes it easier for organizations to adapt to changing market demands and customer preferences.
- Employee Engagement: The emphasis on employee involvement and continuous improvement fosters a culture of engagement and innovation.
Conclusion:
Embracing lean manufacturing principles is a strategic decision that can propel organizations towards excellence in production and operations. By continuously seeking ways to eliminate waste, optimize processes, and enhance value, companies can not only survive but thrive in today's competitive manufacturing landscape. The journey towards lean manufacturing may require commitment and persistence, but the rewards in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction make it a worthwhile endeavor.